Angular模版驱动表单 & 响应式表单
表单的作用:
- 快速收集用户输入信息
- 提供submit、reset等行为支持
- 校验、提交等状态的收集
Angular的表单分类:模版驱动表单、响应式表单(模型驱动表单)
模版驱动表单
https://angular.io/docs/ts/latest/guide/forms.html
直接在组件模版中,通过内置的表单指令绑定到对象属性上。
优点:
- 简单
- 快速
- 不需要太多的编码
缺点:
- 控制能力差
- 不方便添加自定义校验
- 逻辑容易积累在模版中
export class Hero {
constructor(
public id: number,
public name: string,
public power: string,
public alterEgo?: string
) { }
}
@Component({
selector: 'hero-form',
templateUrl: './hero-form.component.html'
})
export class HeroFormComponent {
powers = ['Really Smart', 'Super Flexible',
'Super Hot', 'Weather Changer'];
model = new Hero(18, 'Dr IQ', this.powers[0], 'Chuck Overstreet');
onSubmit() {
// 调用后台服务,保存数据
}
}
<form (ngSubmit)="onSubmit()" #heroForm="ngForm"> <!-- 绑定表单的submit事件 -->
<div class="form-group">
<label for="name">Name</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="name"
required <!-- 自定义校验规则 -->
[(ngModel)]="model.name" name="name" <!-- 双向绑定到组件属性 -->
#name="ngModel"> <!-- 获取FormControl的引用 -->
<div [hidden]="name.valid || name.pristine" class="alert alert-danger"> <!-- 根据输入状态控制提示信息 -->
Name is required
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="power">Hero Power</label>
<select class="form-control" id="power"
required
[(ngModel)]="model.power" name="power"
#power="ngModel">
<option *ngFor="let pow of powers" [value]="pow"></option> <!-- 显示下拉选项 -->
</select>
<div [hidden]="power.valid || power.pristine" class="alert alert-danger">
Power is required
</div>
</div>
<!-- type=submit出发submit事件; 获取整体表单的校验状态 -->
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-success" [disabled]="!heroForm.form.valid">Submit</button>
<!-- 使用form对象的内置方法 -->
<button type="button" class="btn btn-default" (click)="heroForm.reset()">Reset</button>
</form>
</div>
使用模型驱动表单,需要在AppModule中引入FormsModule
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
FormsModule
],
declarations: [
AppComponent,
HeroFormComponent
],
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ]
})
export class AppModule { }
响应式表单的使用:
- 引入FormsModule
- 使用ngModule绑定到组件的属性上
- 使用ngForm和ngModel内置指令获取控制对象的引用
- 使用默认的校验规则
- 使用Angular管理的表单、输入状态来控制提示信息显示
内置校验规则
/**
* Validator that requires controls to have a non-empty value.
*/
static required(control: AbstractControl): ValidationErrors | null;
/**
* Validator that requires control value to be true.
*/
static requiredTrue(control: AbstractControl): ValidationErrors | null;
/**
* Validator that performs email validation.
*/
static email(control: AbstractControl): ValidationErrors | null;
/**
* Validator that requires controls to have a value of a minimum length.
*/
static minLength(minLength: number): ValidatorFn;
/**
* Validator that requires controls to have a value of a maximum length.
*/
static maxLength(maxLength: number): ValidatorFn;
/**
* Validator that requires a control to match a regex to its value.
*/
static pattern(pattern: string | RegExp): ValidatorFn;
/**
* No-op validator.
*/
static nullValidator(c: AbstractControl): ValidationErrors | null;
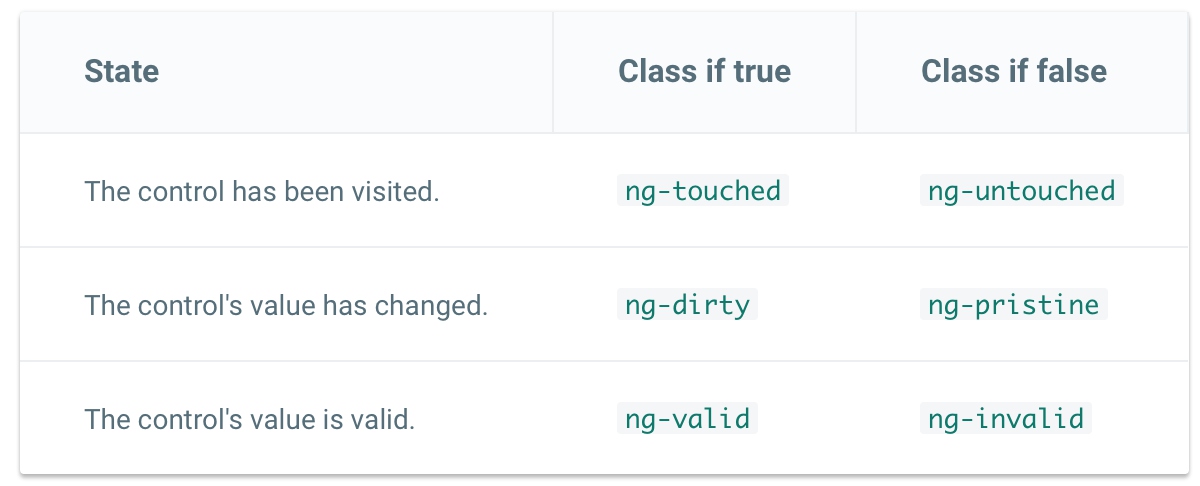
内置的表单状态
响应式表单(模型驱动表单)
在组件中创建和控制表单的控制对象,可以直接向模版中推送数据和监听变化。
相对于模版驱动表单,具有如下优点:
- 使用响应式编程范式
- 灵活、可控
- 状态的推送、获取是同步的
- 便于添加自定义校验规则
- 便于测试
缺点:
- 一定的学习成本
- 增加编码量
this.heroForm = this.fb.group({
name: ['', Validators.required],
address: this.fb.group({
street: '',
city: '',
})
});
<form [formGroup]="heroForm" novalidate>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="center-block">Name:</label>
<input class="form-control" formControlName="name">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="center-block">Street:
<input class="form-control" formControlName="street">
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="center-block">City:
<input class="form-control" formControlName="city">
</label>
</div>
</form>
模块中需要导入ReactiveFormsModule:
imports: [
CommonModule,
ReactiveFormsModule
],
使用响应式表单:
- 组件中通过FormBuilder服务,手动创建FormGroup和FormControl对象,并且指定校验规则
- 模板中通过formGroup和formControlName指令绑定到组件的控件上
可以通过FormControl的API来控制表单的输入控件
/**
* Set the value of the form control to `value`.
*
* If `onlySelf` is `true`, this change will only affect the validation of this `FormControl`
* and not its parent component. This defaults to false.
*
* If `emitEvent` is `true`, this
* change will cause a `valueChanges` event on the `FormControl` to be emitted. This defaults
* to true (as it falls through to `updateValueAndValidity`).
*
* If `emitModelToViewChange` is `true`, the view will be notified about the new value
* via an `onChange` event. This is the default behavior if `emitModelToViewChange` is not
* specified.
*
* If `emitViewToModelChange` is `true`, an ngModelChange event will be fired to update the
* model. This is the default behavior if `emitViewToModelChange` is not specified.
*/
setValue(value: any, options?: {
onlySelf?: boolean;
emitEvent?: boolean;
emitModelToViewChange?: boolean;
emitViewToModelChange?: boolean;
}): void;
/**
* Patches the value of a control.
*
* This function is functionally the same as {@link FormControl#setValue} at this level.
* It exists for symmetry with {@link FormGroup#patchValue} on `FormGroups` and `FormArrays`,
* where it does behave differently.
*/
patchValue(value: any, options?: {
onlySelf?: boolean;
emitEvent?: boolean;
emitModelToViewChange?: boolean;
emitViewToModelChange?: boolean;
}): void;
/**
* Resets the form control. This means by default:
*
* * it is marked as `pristine`
* * it is marked as `untouched`
* * value is set to null
*
* You can also reset to a specific form state by passing through a standalone
* value or a form state object that contains both a value and a disabled state
* (these are the only two properties that cannot be calculated).
*
* Ex:
*
* ```ts
* this.control.reset('Nancy');
*
* console.log(this.control.value); // 'Nancy'
* ```
*
* OR
*
* ```
* this.control.reset({value: 'Nancy', disabled: true});
*
* console.log(this.control.value); // 'Nancy'
* console.log(this.control.status); // 'DISABLED'
* ```
*/
reset(formState?: any, options?: {
onlySelf?: boolean;
emitEvent?: boolean;
}): void;
/**
* Register a listener for change events.
*/
registerOnChange(fn: Function): void;
/**
* Register a listener for disabled events.
*/
registerOnDisabledChange(fn: (isDisabled: boolean) => void): void;
监听页面输入变化
const nameControl = this.heroForm.get('name');
nameControl.valueChanges.forEach(
(value: string) => this.nameChangeLog.push(value)
);
自定义校验规则
创建校验函数
/** A hero's name can't match the given regular expression */
export function forbiddenNameValidator(nameRe: RegExp): ValidatorFn {
return (control: AbstractControl): {[key: string]: any} => {
const name = control.value;
const no = nameRe.test(name);
return no ? {'forbiddenName': {name}} : null;
};
}
响应式表单如何使用?
'name': [this.hero.name, [
Validators.required,
Validators.minLength(4),
Validators.maxLength(24),
forbiddenNameValidator(/bob/i)
]
],
模版驱动表单如何使用?
@Directive({
selector: '[forbiddenName]',
providers: [{provide: NG_VALIDATORS, useExisting: ForbiddenValidatorDirective, multi: true}]
})
export class ForbiddenValidatorDirective implements Validator, OnChanges {
@Input() forbiddenName: string;
private valFn = Validators.nullValidator;
ngOnChanges(changes: SimpleChanges): void {
const change = changes['forbiddenName'];
if (change) {
const val: string | RegExp = change.currentValue;
const re = val instanceof RegExp ? val : new RegExp(val, 'i');
this.valFn = forbiddenNameValidator(re);
} else {
this.valFn = Validators.nullValidator;
}
}
validate(control: AbstractControl): {[key: string]: any} {
return this.valFn(control);
}
}
<input type="text" id="name" class="form-control"
required minlength="4" maxlength="24" forbiddenName="bob"
name="name" [(ngModel)]="hero.name" >